|
Radon gas, a silent and potentially hazardous intruder in homes, poses a significant health risk to families. As a homeowner, it's crucial to take proactive measures to protect your loved ones Radon is a gas we can't see or smell, but it can harm our health. It comes from the ground when uranium in soil breaks down. If it gets into our homes through cracks, it can become a risk. The problem with radon is that breathing it in for a long time can cause lung cancer. Even though we can't detect radon with our senses, it's important to check our homes for it. Protecting ourselves is easy. Homeowners can use testing kits, and professionals can help too. If levels are high, we can fix it by improving ventilation or using special systems. Taking these steps makes our homes safer, lowering the chances of health problems from radon. Regular checks and actions keep us and our families safe from this hidden danger. Here are five essential steps to shield your family from radon gas exposure
Proven Technology: Out of the various radon measurement devices tested, Radon test kit technology consistently outperformed the rest. Our customers have experienced no issues, endorsing its effectiveness. Global Reliability: Whether you reside in Canada, the United States, or anywhere globally, our Radon Test Kit is tailored to provide accurate results, offering peace of mind regarding your home's radon levels. Responsive Lab Services: Understanding the urgency of timely results, we appreciate the quick and responsive services of the lab, ensuring you receive accurate radon measurements promptly. Why Test for Radon: Radon, a radioactive gas, can seep into homes and pose significant health risks. Performing a one-time radon test is crucial to understanding and mitigating this hidden danger. 1. Initiate Testing with a Certified Radon Test Kit The first line of defense most crucial step in keeping our homes safe. It's like the first shield that protects us from potential harm. To do this, we can use certified radon test kit. One such kit is the Radon Test Kit by Simon Air Quality. This kit is like a tool that helps us check how much radon is in our homes. It's important because radon is a gas we can't see or smell, and it might be in our houses without us knowing. By using the Radon Test Kit, we can accurately measure the levels of radon inside. This measurement is like a starting point, a baseline, to understand the possible risks. It's a simple action with a significant impact. Once we know the radon levels, we can take other steps to make our homes safer. It's a bit like getting a heads-up about something potentially harmful and then figuring out the best way to protect ourselves and our families. Knowledge is indeed our first and powerful defense against radon. We have two types of tests – short-term and long-term. Let me tell you a bit about them in simple terms. So, the short-term radon test kit is like a quick check. It gives us results pretty fast, giving us immediate insights into the radon levels. It's like taking a snapshot of the situation at that moment. Now, the long-term radon test kit is like a continuous check. This approach is helpful because it can show us patterns or trends in how radon levels go up or down. Early detection of these patterns is like having a heads-up – we can know about potential issues before they become significant. So, choosing long-term radon testing is like having a continuous guardian in our homes, making sure we stay informed about any changes in radon levels. It's all about staying one step ahead to keep our homes safe. 3. Simplify with DIY Radon Testing Using a DIY radon test is like doing a simple and easy check for radon in your home. DIY means "do it yourself," and it's something you can do without needing help from a professional. It's as straightforward as using a kit, and one such kit is offered by Simon Air Quality. Imagine it like this: You have a special tool (the radon test kit) that helps you find out if there's radon in your home. You don't need an expert; you can do it on your own. It's like solving a little mystery about the air in your house. These DIY kits are designed to be easy for homeowners. You follow some simple steps, and the kit does the rest. It's like a helpful friend guiding you through the process. 4. Utilize Radon Calculators for In-Depth Assessment Enhance your understanding of radon concentrations by using radon calculators. These tools provide valuable insights, helping you assess potential risks and determine the necessary precautions. A proactive approach to radon calculations contributes to a more comprehensive protective strategy Conclusion Protecting your family from radon gas involves a combination of awareness, testing, and informed decision-making. By initiating testing with a certified kit, understanding the associated health risks, opting for long-term monitoring, simplifying the process with DIY testing, and utilizing radon calculators, you take significant strides toward creating a safe and healthy living environment for your loved ones. Prioritize your family's well-being by implementing these essential steps today.
0 Comments
Introduction: The air we breathe plays a vital role in our well-being, and when it comes to the safety of our homes, understanding potential threats is key. Radon, a colorless and odorless gas, can accumulate in homes and pose serious health risks. Choosing the right radon test kit is a crucial step in ensuring a safe and healthy living environment. In this blog, we'll explore the importance of radon testing, the different types of DIY radon test kits available, and how to make an informed choice for your home. The Need for Radon Testing: Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can seep into homes through the ground. Prolonged exposure to elevated levels of radon can lead to serious health issues, including lung cancer. The only way to know if radon is present in your home is through testing. Taking a proactive approach to radon testing allows you to identify and address potential risks, ensuring the well-being of your household. DIY Radon Test Kit | Long-Term: A "DIY Radon Test Kit | Long-Term" refers to a do-it-yourself radon testing solution designed to assess the concentration of radon gas within a home over an extended period. Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can enter homes through the ground, posing health risks if present in elevated levels. The purpose of long-term radon testing is to obtain a more accurate representation of the average radon concentration in the indoor air over an extended timeframe, typically lasting three months or more. Here's a breakdown of the key features and aspects of a DIY Radon Test Kit for Long-Term use: Testing Duration: Long-term radon testing involves leaving the test kit in the home for an extended period, allowing it to capture variations in radon levels over time. The recommended duration for long-term testing is usually three months or more. Comprehensive Analysis: The extended testing period provides a more comprehensive and reliable analysis of radon levels compared to short-term testing. It offers a better understanding of the average radon concentration in different seasons and under varying environmental conditions. Ease of Use: DIY radon test kits are designed for ease of use, allowing homeowners to perform the test without the need for professional assistance. Clear instructions guide users through the placement of the kit and the retrieval process. Accurate Results: Long-term testing is considered more accurate for assessing the overall radon exposure in a home. The results help homeowners make informed decisions about potential radon mitigation measures if elevated levels are detected. Sampling Method: The test kit typically uses a passive sampling method, where it absorbs radon from the air over the testing period. After the designated timeframe, the kit is retrieved, and the collected samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis. Brand-Specific Features: Different brands may offer variations in features, such as prepaid postage for sending samples to the laboratory, digital readings for immediate results, or additional resources to help users interpret their results. Brand Reliability: It's crucial to choose a DIY radon test kit from a reputable brand known for accuracy and reliability. Brands like Guardian Air provide quality test kits that adhere to industry standards. DIY Radon Test Kit | Short-Term: A "DIY Radon Test Kit | Short-Term" refers to a do-it-yourself radon testing solution designed to assess the concentration of radon gas within a home over a relatively brief period. Radon is a colorless and odorless radioactive gas that can seep into homes from the ground, potentially reaching harmful levels. Short-term radon testing provides a quick snapshot of radon levels in the indoor air, typically lasting for a period of two to seven days. Here's an overview of the key features and aspects of a DIY Radon Test Kit for Short-Term use:
Testing Duration: Short-term radon testing involves leaving the test kit in the home for a brief period, usually ranging from two to seven days. The shorter testing duration provides a rapid assessment of radon levels, making it suitable for those who want quick results. Quick Results: One of the primary advantages of short-term testing is the swift turnaround time for results. Homeowners can receive results within a shorter timeframe compared to long-term testing, allowing for prompt action if elevated radon levels are detected. Initial Assessment: Short-term testing is often used as an initial assessment to quickly determine whether further investigation or mitigation measures are necessary. It provides a snapshot of radon levels during the specific testing period but may not capture the seasonal variations seen in long-term testing. Ease of Use: DIY radon test kits are designed to be user-friendly, allowing homeowners to conduct the test without the need for professional assistance. Clear instructions guide users through the placement of the kit and the retrieval process. Sampling Method: Similar to long-term testing, short-term testing typically uses a passive sampling method where the kit absorbs radon from the air during the testing period. After the designated timeframe, the kit is retrieved, and the collected samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis. Brand-Specific Features: Different brands may offer variations in features, such as prepaid postage for sending samples to the laboratory, digital readings for immediate results, or additional resources to help users interpret their results. Brand Reliability: Choosing a DIY radon test kit from a reputable brand is essential to ensure accurate and reliable results. Brands like Guardian Air provide trustworthy test kits that meet industry standards. Conclusion: In the quest for a safe and healthy home, choosing the right radon test kit is a crucial step. Whether opting for a DIY Radon Test Kit | Long-Term or a DIY Radon Test Kit | Short-Term, the key is to prioritize your testing needs and preferences. Breathe easy by taking proactive measures to understand and mitigate potential radon risks, ensuring that your home remains a haven of well-being for you and your loved ones. In the pursuit of a safe and healthy home environment, staying informed about potential risks is crucial. Radon, an odorless and colorless gas, poses a serious health threat when present in elevated levels. To empower homeowners in safeguarding their families, DIY short-term radon test kits have become invaluable tools. In this blog, we'll explore the significance of short-term radon testing, the ease of using DIY kits, and how this quick solution contributes to home safety.
Understanding Short-Term Radon Testing: Radon testing is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy living space. Short-term testing involves using a radon test kit for a brief period, usually two to seven days. While it may not provide the full picture of year-round radon levels, short-term testing is an efficient way to identify potential issues quickly. It serves as an initial step, helping homeowners make informed decisions about their indoor air quality. The DIY Advantage: DIY short-term radon test kits offer homeowners a convenient and cost-effective solution to assess radon levels in their homes. These kits typically include everything needed for the testing process, from instructions to the necessary testing materials. Let's delve into the advantages of opting for a DIY approach: Cost-Effective: DIY kits are budget-friendly compared to hiring professionals for radon testing. This cost-effective option allows homeowners to take proactive steps toward a safer living environment without breaking the bank. Ease of Use: DIY radon test kits are designed with simplicity in mind. Clear instructions guide users through the testing process, making it accessible for individuals without specialized knowledge. The user-friendly nature of these kits ensures that anyone can perform the test with ease. Quick Results: Short-term testing provides rapid results, offering homeowners a quick assessment of their current radon levels. This swift turnaround time enables prompt action if elevated radon levels are detected. Empowerment Through Knowledge: By conducting a DIY short-term radon test, homeowners gain valuable insights into their indoor air quality. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about potential mitigation measures and long-term monitoring. Steps for DIY Short-Term Radon Testing:
Investing in a DIY short-term radon test kit is a proactive step toward creating a safer and healthier home environment. Quick and easy to use, these kits provide homeowners with valuable information about their indoor air quality. With the knowledge gained from testing, individuals can take appropriate measures to mitigate radon risks and ensure the well-being of their loved ones. Don't compromise on home safety – opt for a DIY short-term radon test kit and take the first step towards a healthier living space. IntroductionIn the quest for a healthy and safe home environment, many dangers can go unnoticed. One such silent threat is radon gas, a colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas that can seep into homes through the ground. Prolonged exposure to elevated radon levels poses serious health risks, making it crucial for homeowners to take proactive measures. Enter Guardian Air – a solution designed to detect this unseen threat and empower individuals to create a healthier living space. In this comprehensive blog, we'll explore the importance of radon testing, the convenience of using radon test kits, and how Guardian Air plays a pivotal role in ensuring your home remains a haven of well-being. Understanding the Radon ThreatRadon is a natural radioactive gas that forms from the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water. It can enter homes through the ground and accumulate to dangerous levels, posing a significant health risk. Long-term exposure to elevated radon concentrations is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The World Health Organization (WHO) also recognizes radon as a major cause of lung cancer worldwide.
The Importance of Radon Testing: Given the potential health hazards associated with radon exposure, regular radon testing is crucial for homeowners. Testing allows you to assess the radon levels in your home and take necessary steps to mitigate the risks. Long-term radon testing is especially valuable, providing a more accurate representation of the average radon concentration over an extended period. DIY Radon Testing Made Simple: Guardian Air recognizes the need for accessible and user-friendly radon testing. With their DIY radon test kits, homeowners can conveniently and accurately measure radon levels within their living spaces. These kits are designed for ease of use, allowing you to take control of your indoor air quality without the need for professional assistance. Steps for DIY Radon Testing:
What sets Guardian Air apart in the realm of radon testing is not just the efficacy of their test kits, but also their commitment to health and well-being. By offering accessible and reliable DIY radon test kits, they empower individuals to take proactive measures in creating a healthier home environment. Radon Test Kit Near Me – Convenience at Your Fingertips: For those searching for "radon test kit near me," Guardian Air ensures accessibility. Their products are readily available, and the process is designed to be user-friendly. Take the first step towards a healthier home by finding a Guardian Air radon test kit near you. Understanding Radon Levels – Bq/m3 to Pci/l Conversion: Understanding radon levels is essential for assessing potential health risks. Guardian Air's radon test kits provide readings in Becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m3). If you come across measurements in PicoCuries per liter (Pci/l), it's crucial to understand the conversion. Guardian Air includes helpful resources and a radon calculator to facilitate this conversion, ensuring that you can interpret the results accurately. DIY Radon Testing – A Cost-Effective Solution: One of the significant advantages of using Guardian Air's radon test kits is the cost-effectiveness of the DIY approach. By conducting your radon testing, you not only save on professional testing fees but also gain a deeper understanding of your home's radon levels. Conclusion: In the pursuit of a healthier home, Guardian Air emerges as a reliable ally in the battle against the unseen threat of radon gas. With their user-friendly DIY radon test kits, homeowners can take charge of their indoor air quality and make informed decisions to mitigate potential risks. By offering accessibility, reliability, and a commitment to health, Guardian Air ensures that every individual can create a living space that prioritizes well-being. Don't let the unseen threat of radon compromise your home – choose Guardian Air for a healthier living environment. A radon mitigation system is used to reduce radon levels in your home; however, it will not work instantly. There are different factors to consider when trying to determine how long it will take for your radon mitigation system to work in your home. Standard systems are effective within 24 hours of installation, but in order to get an accurate reading, it's best if you wait for at least 72 hours before starting a new radon measurement. What is Radon Mitigation?Radon mitigation is the procedure of reducing risk associated with radon gas by extracting the radon gas straight from the ground underneath your home, which results in greatly reducing the radon concentration. This gas is colorless and doesn't have a smell, so it's impossible to know how much radon is present through the use of your human senses alone. Since radon gas is one of the leading causes of lung cancer, it is essential to get it checked once in a while. There are many ways to test radon levels, including getting an assessment with a certified Radon Contractor who will take readings throughout your home. If you don't want to consult a certified expert, you can always do the radon testing yourself. How Long Does It Take To Work?The answer to this question depends on a few factors, including the type of system installed and the level of radon in your home prior to installation. Generally speaking, however, it can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks for a radon mitigation system to work effectively. If you have a passive system, it may take longer to see results as the system relies on natural airflow and pressure differential to draw out the radon gas. An active system, on the other hand, uses fans to force air through the system and out of your home, so you will most likely see results quicker. Of course, the level of radon in your home will also play a role in how long it takes for the mitigation system to work. If you have a very high level of radon, it may take longer to see a significant reduction. However, even if it takes a little bit longer, a mitigation system will eventually bring the level of radon down to a safe/low level. If you're concerned about the amount of time it is taking for your mitigation system to work, the best thing to do is to contact a professional. They can test your home's radon levels. They can also inspect your radon mitigation system for any deficiencies and then let you know if the system is working as it should. Radon mitigation systems reduce radon levels in the air by pulling radon gas up from the ground below basement or crawl space through pipes and into the fresh air outside your home. The typical radon mitigation system will begin lowering levels within 24 hours and continue as long as the fan runs. These systems may also help lower basement humidity by redirecting the moisture from the ground and expelling it to the outside along with the radon gas. Factors That Influence the Speed of Radon RemovalIn an ideal scenario, removing radon from the home would begin hours after testing is complete and the appropriate mitigation equipment is installed. That isn't always the case, though. Radon mitigation might be delayed due to a few independent factors: Type of Radon TestQuick tests can only be conducted at your house for a few days. If you choose to use a radon monitor to perform a quick test, you can get an instantaneous reading of the radon concentration in your home during that period. Long-term testing, which assesses radon levels yearly, can be time-consuming because they take months to complete. The Age and Size of The HomeOlder homes with many cracks and crevices can have higher infiltration rates These cracks and crevices may be in places where people cannot see and/or access, thus making it harder for mitigators to find all areas where the gas can enter. Previous Attempts at Mitigating Radon Levels in The HomeSometimes, if a previous attempt has not been successful, there will be a small improvement over time. For example, if just sealing off some cracks does not stop gas from seeping through other cracks in the same foundation, installing an active sub-slab depressurization system would be a viable solution. Alternatively, placing the room, in which the cracks are located, under constant positive pressure will work as well. External Radon SourcesIf radon comes from a location other than your house, such as water flowing through the ground into wells, installing a mitigation system within said well would be beneficial. Mitigation System TypeMost radon mitigation systems are designed to be set up in a day. More powerful mitigation systems, or more complex systems, may take longer to set up. In addition, even when the system is installed correctly, homeowners should still regularly monitor their radon levels because they could fluctuate depending on external conditions like soil composition, any nearby construction, abnormal weather patterns, or changes in pressure differentials. How Soon After Mitigation Can You Retest For Radon?Once the radon mitigation system is installed, it is wise to keep testing. At the very least, you should allow twenty-four hours for the radon levels in your home to decrease after installing a new system. The retest must be completed no more than thirty days after the installation. Generally, if the radon level falls below 4 pCi/L (or 200 Bq/m^3 if you are in Canada), there is little need to retest. However, suppose the reading remains above 4 pCi/L (or 148 Bq/m^3). In that scenario, you will need to hire an expert contractor who can determine what additional steps need to be taken before resuming any form of indoor activity, such as construction or using utilities. FAQsHow Much Does Radon Mitigation Process Cost?The price depends on many factors, mainly the region and state where you live. The cost of radon reduction ranges typically from $750 to $2,500, but the price might go as high as $7,000 for a big home or property with many foundations. How Do You Know If The System Is Working? If you want to check the functionality of your radon mitigation system, use the u-tube manometer. Observe the contents of the tube. There is no internal pipe pressure if the readings are identical on both ends. If the fan isn't pulling the air in, your radon mitigation system isn't functioning. Are Radon Mitigation Systems Effective 100% Of the Time? The EPA has found that they have a 99% success rate in certain situations. If you've had radon mitigation done in your house, but if the readings remain high, or roughly at around 4 pCi/L (or 148 Bq/m^3), you chose the wrong radon contractor. This amount of radon in a home is a trigger point. In that case, we suggest you consult a different, certified contractor.
Radon is a radioactive, natural gas that is colorless, tasteless, and odorless. It is formed in rocks and soil when small amounts of uranium begin to decay. Owing to heat and air pressure, it rises up into the air as particles. It has 136 neutrons. In this article, we will tell you everything you need to know about the element radon, and its neutrons. A Breakdown of RadonRadon is one of the most common radioactive gasses because it can be found in soil and rock all over the planet. It is otherwise known as radioactive decay, and it stems from radium. Radon is a type of noble gas that is formed in soil when radium begins to decay. Some landscapes are more prone to radon particles in the air, and those living in homes where radon levels are on the higher end of the scale have to be mindful of regular testing and therefore take various measures to control the exposure to ensure it doesn’t put their health at risk. Radon on the Periodic Table
Basic Information About Radon
What are Neutrons?A neutron is a type of particle found in the nucleus of every atom, with the exception of simple hydrogen. A neutron has no electrical charge, so it is considered ‘neutral’ - hence the name. It differs from a proton because it has a greater mass and is denser. Is Radon Dangerous?Radon is a radioactive gas, which, in large doses, can be extremely harmful (and sometimes fatal) to humans. Radon is fine in small doses. Because it is found in both rock and soil, which makes up inhabitable human land, there’s no way to avoid it entirely. However, when radon levels become too high, they can cause damage to our lungs that may eventually result in lung cancer. It is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Radon Levels - When Should We Be Concerned?Radon is measured differently depending on where in the world you live, meaning danger levels depending on what country you’re in.
If so, you may need to conduct more regular household tests to ensure your safety. How are We Exposed to Radon?As radon is a radioactive gas that is emitted from rock and soil, it rises up into our homes and workplaces, and we breathe it in without realizing it. Once the decomposed molecules of radon enter our lungs, they continue to decay, which further releases more radiation, which is now directly in our systems. However, to be clear, while most of us breathe radon every day, this doesn’t necessarily mean we are in harm’s way. This is the importance of testing. How to Test for RadonThe good news is testing for radon in your property is easy and inexpensive. You can either hire a professional company to do this for you (which will be the more costly option of the two) or purchase a short-term or long-term DIY test kit and test your home yourself. Short-Term Radon Test KitShort-term radon test kits are designed for those who would like to check the radon levels in their space quickly. Please note, however, the minimum amount of time a short-term radon test kit can be performed is 2-10 days, depending on the radon detector you use. If your home or workplace has a basement, the best place to put your radon detector is in the crawl space above your basement. Long-Term Radon Test KitA long-term, DIY radon test kit will need to be performed for 90 days or longer. This is a useful option because radon levels fluctuate all the time, so a longer test period will allow you to monitor those fluctuations better. As with the short-term test kit, the best place to put the detector is in the crawl space above your basement. If you don’t have a basement, however, the ground floor is a good choice. For those in high-story apartment blocks, you can opt to place the detector in your kitchen, bedroom, or living room. This way, you will be able to see if the radon levels are reaching you. Both the short-term and long-term test kits are environmentally-friendly, deployed all over the world, and the results are analyzed by a highly-accredited lab. There are no hidden fees, and the turnaround time for results is much quicker than that of store-bought DIY radon tests. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)How can I keep myself safe from radon?Non-smokers are in a better position to radon exposure than smokers, as their lungs are less damaged, so not smoking is a good place to start. If you live in high-radon areas, you can install a radon mitigation system in your home to regulate the levels in your home. Keeping your space well-ventilated is also a good way to lessen your exposure. How does radon enter my home?Radon enters through openings in the floor, such as cracks, gaps around pipes, floor drains, wall cavities, and so on, and rises upwards. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, so while we may not know it is there, we may still be breathing it in. What is the science behind radon?Radon is one of the chemical elements with the "Rn" symbol. It is arguably the most common chemical element because its decay chain occurs within soil.
There are 37 stable isotopes, and it belongs to the radium and uranium decay chain. Some professionals may refer to radon gas as alpha decay, which is a type of radioactive decay that involves an atomic nucleus which emits alpha particles, otherwise known as helium nucleus. The most stable isotope of radon gas is 222Rn, which has a half life of 3.832 days. It is a zero valence noble gas, and despite being a radioactive gas, it isn't very chemically reactive. Radon gas is probably the last thing on your mind when you think about your home. After all, it's not something you can see, smell or taste, so it's easy to forget that it's even there. But radon gas is a real threat to your family's health, and it's important to take the necessary steps to mitigate it. As the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, radon gas is estimated to cause about 21,000 deaths each year in the United States. That's why it's so important to protect you and your family by having a radon gas mitigation system in place, in your home. But with so many different types of mitigation systems on the market, it can be tough to know which one is right for your home. Here's a quick guide to the best radon gas mitigation systems for your home, so you can keep your family safe from this invisible threat. What Is a Radon Gas Mitigation System?By now, you've probably realized how big of a threat radon gas can be and that a radon gas mitigation system is a must in any home. But what, exactly, is a radon gas mitigation system? A radon gas mitigation system is designed to remove radon gas from your home and keep it at safe levels. Technically it won't remove the radon from your indoor. Technically it extracts the radon from the ground, which results in a significant decrease in indoor radon concentrations since radon comes from the ground. There are a few different types of systems, but they all work to achieve the same goal: reduce the amount of radon gas in your home. There are different types of systems because there are different methods one can use to mitigate radon. Radon gas mitigation systems work by either drawing air from your home and venting it outside, sealing radon out from your home, or by extracting the radon from the source, AKA the ground. This process helps to keep the levels of radon gas in your home at a safe level, so you and your family can breathe easy. The Best Radon Gas Mitigation Systems for Your HomeNow that you know a little bit more about radon gas mitigation systems, let's take a look at the best ones for your home. Active Sub-slab Depressurization (ASSD)Active sub-slab depressurization is one of the most effective radon gas mitigation systems on the market. Also known as sub-slab depressurization, this system works by drawing air from beneath your home's foundation and venting it to the outside. This system is most effective in homes with a poured concrete foundation. Even if the basement is completely finished, ASSD will still work effectively. One or multiple suction pipes are installed in the basement after coring a hole through the concrete slab. They are then connected to a radon fan that draws air from beneath the foundation before venting to the outside. This process helps to keep the levels of radon gas in your home at a safe level. ASSD systems are extremely effective - the most effective type of system that exists currently. Regarding the cost, when comparing it to a furnace or HRV, it is significantly cheaper. Passive Sub-Slab Depressurization (PSD)Passive sub-slab depressurization is similar to ASSD, but doesn't require a vent fan. Instead, this system relies on the natural pressure differential between the indoor and outdoor air to draw air from beneath the foundation and vent it to the outside. PSSD systems are associated with radon-resistant construction techniques, which are designed to prevent radon gas from entering your home in the first place. These construction techniques can be used in new construction settings or during a home renovation. PSSD systems are effective, though not as effective as ASSD systems. They're also less expensive to install and require very little to no maintenance. Soil SuctionSoil suction is a type of radon gas mitigation system that's typically used in homes with crawlspaces. This system works by drawing air from the crawlspace and venting it outside. One or multiple suction pipes are installed in the crawlspace and are connected to a radon vent fan that draws air from the crawlspace and vents it to the outside. This process helps to keep the levels of radon gas in your home at a safe level. Soil suction systems have proven to be very effective at reducing radon levels in homes, especially when they are combined with a membrane sealed overtop of the soil and/or rock. They can be trickier to install compared to an ASSD system. Block Wall SuctionBlock wall suction is similar to soil suction, but it's typically used in homes with block walls instead of crawlspaces. This system works by drawing air from the spaces between the block wall and the foundation and venting it to the outside. Basement homes that have hollow block foundation walls can benefit from this type of system. By utilizing a fan and ductwork, this system draws air from the block walls and then vents the radon gas to the outside, helping to keep the concentration levels of radon gas in your home below the guideline. Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV)Older homes that don't have good ventilation can benefit from a heat recovery ventilation (HRV) system. This type of system helps to improve the air quality in your home by drawing fresh air in from outside while simultaneously exhausting stale indoor air to the outside. HRV systems are typically used in homes that are built so air tight that they require a mechanical means of ventilation. These systems are also used as solutions in homes that have other indoor air quality issues, such as mold or radon. As mentioned earlier, HRV systems work by drawing fresh air from the outside and exhausting stale, indoor air. The fresh air is drawn through a heat exchanger, which helps to cool or heat the air before it enters your home. This process helps to not only improve the air quality in your home, but it can also help to reduce your energy bills. Wrapping UpNo one wants to be exposed to radon gas, but unfortunately it's presence in homes is a concern worth addressing.
Luckily, there are a variety of effective radon gas mitigation systems that can help to keep your family safe. The 5 systems described above are some of the most popular and effective systems on the market. If you live in Ontario and you are someone in need of a radon mitigation system, contact Simon Air Quality. They would be happy to help you. They are C-NRPP certified with years of experience removing radon from buildings all over Ontario. Chance to know what?
Your chance to find out just how much radioactive gas is lurking inside your home. Because no matter where you live, radon gas will live there too. There is no way to be 100% free of it. So the question becomes... "Okay, well then how much of it am I living with in my house?" And maybe a second question would be... "Well how much of this radioactive gas can I handle before it starts to harm me?" Before we answer those questions however, we first need to tell you about Susan and Ashley - two middle aged, married women with families. You see both of them have something in common. Something unfortunate for them, but an eye opener for everyone else. A tragedy for these two individuals and their families, yet a new revelation and appreciation for those who learned from it. These two otherwise healthy individuals with no bad habits, like smoking for example, were diagnosed with lung cancer. It grew and spread throughout their whole body. The battle was long and rough, but the cancer was too strong and they both passed away as a result. The coincidence you see, was that each one lived in a house (2 very different houses), which both got tested for radon following their passing. It was revealed that, at the time, both houses contained incredibly high radon concentrations - over 10,000 Bq/m3 or roughly 271 pCi/L. Again, they were otherwise healthy people who didn't smoke a day in their lives, but yet they died because a radioactive gas, that we cannot see, touch, hear or feel, gave them aggressive cancer. So if you don't know what radon is or if you have never heard of it before, this is your chance to learn more about it. Our DIY Radon Test Kit includes information about where radon gas comes from, what you can do to protect yourself from its harmful effects and much, much more. No one is exempt or invincible when it comes to radon, but... At least we have the right tools and equipment available to us that can measure radon gas. And the right equipment to mitigate the risk associated with radon right down to a point where it becomes no concern to our health. So if you measure the amount of radon in your home and it's discovered that you have less than favorable results, it's okay. We can provide you with the resources, knowledge, references, and contacts necessary for you to tackle your radon issue and eliminate its risk permanently. That's right, permanently! Never again will you have to address radon concerns after that. Unless of course you move to a different location. Get this radon measurement kit one time. Measure your house one time. If needed, mitigate your house one time. Tell all your friends and family about your adventure. Live a life free of lung cancer because you proactively addressed radon using the #1 radon test kit available. They say knowledge is power, but that's not 100% accurate is it? Knowledge coupled with taking action is true power. So seize the power. This is your chance. Order a radon test kit today. You will be happy you did. Radon gas is a silent killer - one of those things that can be in your home or office, but you may not know about it until it does the damage. The affects can be very severe - according to various health authorities, radon is the biggest cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. If you have recently built or moved into any building, it's imperative to check for radon. To do that, you'll need a radon test kit. This article discusses what radon test kits are, when they are used and how to use them. IntroductionA radon test kit is a device used to measure the amount of radon gas in the indoor air. You set it up, allow it to detect radon gas for a predetermined amount of time, and then mail it to a certified lab capable of analyzing it. The lab will conduct a test and return the results to you via mail or email. If you do a short-term radon measurement and detect high levels, it's recommended you do a long-term measurement afterwards to confirm. If you get the same/similar results the second time, it's time to take action. Why Do You Need to Test for Radon?The World Health Organization identifies radon as a carcinogenic agent that can cause lung cancer. About 25,000 and 3,000 people die from radon annually in the United States and Canada respectively. While harmful, radon has no flavor, odor, or color; therefore, you'll need to do a special test to detect the presence of this gas. Now remember, radon has been found in every part of the world and can build up in any building, anywhere. So, radon testing is something you can't afford to miss, for your family's safety. Types of Radon Test KitThere are two types of radon testing kits. Let's explore them. Short-Term KitA short-term test will take anywhere between 2 and 90 days. The type of short-term radon test kit we provide takes at least 10 days. It's mostly used as a screening test to determine if a long-term measurement is required; however, sometimes people cannot wait 90 days to receive a final test result. For example, realtors have a timeline to follow and are often pressured to get a list of tasks done before the closing date. They absolutely cannot wait 90+ days to receive results, so they depend on the results that come from performing a short-term radon test. Long-Term Kit A long-term test kit measures the radon levels in an area for at least 90 days and up to a year. It is more accurate than a short-term test because it exposed to a greater sample size of radon gas; therefore, organizations like Health Canada, for example, only recognize the results derived from a test like this. On the other hand, the E.P.A. will recognize both short-term and long-term results. Which Kit Should I Use?Well, you should first conduct a short-term test to get a rough idea about the radon levels in your house. If the concentration is really high, then you should install a radon reduction system right away. If the short-term test results are just under or just above the guideline, then it would be a good idea to then perform a long-term radon measurement. You can also conduct a radon measurement - either short-term or long-term - after a radon mitigation system has been installed in your house so that you know it is working effectively. Can I Do My Radon Testing?Of course you can conduct a radon test on your own. You do not have to be licensed or certified to do so; however, since there are many steps and possibilities of committing an error, you may better be off calling a radon measurement professional if you want to make sure it's done right. Also, depending on where you live, you may need to hire a professional to do radon testing for real estate transactions. Be careful about this - look into this prior to the start of any test. How To Conduct a Radon TestThis depends on the type of kit you have bought. You'll need to look at the user's guide and follow the instructions accordingly. Most testing kits consist of a radon detector, a form, instructions, some literature on radon, and return mailing packaging to ship off the sample. You place the detector in the basement and leave it for a minimum of 48 hours or longer, depending on the type of test. Finally, you send the sample to the lab and get the results. You will receive the results by mail, email, or both. Where Can I Get a Radon Test Kit?Radon testing kits can be purchased from local hospitals and stores. If you live in the USA, you can buy them from your state's national radon program services website. Some tests require additional testing fees to be paid before the kits are mailed to the lab. In addition, you can buy discounted test kits from our website for more convenience. We deliver everywhere in the USA, Canada, and soon to be all over the world. Ways To Make A Radon Test More EffectiveHere are some steps you can follow to get a more accurate reading of your home's radon level, especially if you plan on doing a short-term radon test:
More FAQs Related to Radon Test KitsHere are some more frequently asked questions about radon test kits... Are Radon Test Kits and Monitors the Same?No, test kits are not the same as continuous radon monitors. Continuous monitoring devices are more expensive and are generally used by professionals (although consumers are free to use them as well) to test the average radon level in the house. While accurate, they may be a luxury you don't need. What Is a Passive Radon Detector?You may often hear the phrase 'passive radon detector' when looking for a test kit. Don't be confused. It's just another name given to a detector in a radon testing kit that doesn't use electricity. What to Do if I Find Radon Gas in My House?The Environmental Protection Agency and Health Canada recommend installing a radon reduction system if you discover a high concentration of radon in your home. A high concentration would be considered any concentration above the guideline you choose to follow.
Studies show that nearly 1 out of every 15 houses in the US and 6.9 % of houses in Canada have elevated radon levels. This radioactive gas is fairly common worldwide, with 56 nations already responding to the W.H.O. radon survey. Many people know that radon causes lung cancer but don’t know its source. If that’s the case for you as well, this article sheds light on everything you need to know about the origin of radon gas, including what it is, where it comes from, how it causes cancer, and other related FAQs. What Is Radon Gas?Radon is a radioactive gas produced by the decay of uranium, thorium, or radium in soil, rocks, and underground water. As you can see, all the particles that can create radon are naturally occurring and can be found everywhere in the world, making this gas very common. Radon doesn't have any particular taste, feel, or smell. You'll need to do a special test to find its concentration in your home or office. Furthermore, radon can also exist outdoors, even if the concentrations aren’t as high as inside a building. How Does Radon Get Into Our Homes?Radon can enter buildings in two ways: By Rising From the SoilThe air pressure inside a building is lower than in the soil, making air and gas move from high pressure to low pressure. In other words, the vacuum in the house sucks the gas from the soil when created, allowing it to enter from small cracks in the foundation. Other places from where radon can get into buildings include hollow block walls, dirt floors, sump pumps opening in floor drains, and openings in pipes, sewers, and other utility connections. Via Well WaterHouses that use well water are susceptible to radon. This gas can mix in the water and be released into the air while showering or dishwashing. You may also sometimes end up ingesting radon if you drink water from the tap. However, it's not a big concern in itself. But again, the implications aren't in your favor - if the drinking water in your home has radon, there's a high probability that the air has it too. Note: Drinking water with radon can cause stomach cancer in some rare cases, but the risk isn't as much as cancer in the lungs caused by radon gas in the air. Does Radon Exist in Every Building?Yes, almost every residential or commercial building has radon gas; however, not all of them have high radon concentrations. While there is no safe quantity for radon, according to the WHO, levels of less than 2.7 PCI /l (100 Bq/m3) can be considered normal. If the radon concentration is higher, you should take action to mitigate your risk. Why Are Radon Levels Higher Indoors Than Outdoors?With its massive volume, outdoor air dilutes radon gas down to a concentration that is negligible. Furthermore, with passing time, more and more radon can accumulate inside a building, increasing the danger. When outdoor air is introduced to the indoors, this fresh air will dilute the indoor radon concentration. What Makes Radon Cause Lung Cancer?Radon is considered the second leading cause of lung cancer and the biggest cause of the disease in non-smokers. As we discussed earlier, it is a radioactive gas. This gas releases tiny alpha particles into the air, which can collect in your lungs when inhaled. These particles eventually release tiny bursts of energy, slowly damaging your lung tissue and increasing your risk of developing lung cancer. Does Radon Cause Other Types of Cancer?Based on existing evidence, lung cancer is the only disease that can be caused by inhaling radon. Rarely, radon can cause stomach cancer when ingested. This phenomenon is similar to what happens in the lungs - consumed radon can diffuse into radioactive particles that can stick to, and damage the stomach linings, eventually causing cancer. Please note that more research is needed on this topic because some studies associating radon and stomach cancer have mixed results. What Types of Houses Are More Likely to Have the Radon Problem?Honestly, there is no one common answer to this question. Generally, homes with slab-on-grade foundations and crawl spaces are more likely to have radon since they have many openings that allow the gas to enter. Furthermore, the risks of radon exposure can be high for people that use their basement as a living space. But again, the radon levels in the indoor air can depend on many other conditions and variables, like the presence of radioactive materials in the soil, building materials, etc. And remember, even neighboring houses can have very different radon levels. Hence, it's difficult to generalize, and every homeowner should be wary of radon. Every individual house/unit/dwelling needs to have a test done to determine it's risk level associated with radon. How Can I Know the Radon Level in My House?You can use either one of these amazing radon test kits to find the amount of this radioactive substance in your house. These kits provide you with a hockey puck looking device to be placed in the basement or a room you use often. Depending on the type of the type of kit you use, you will wait between 2 and 90 days or between 90 days and a year before sending the detector to the lab for analysis. On the other hand, you can also contact a professional radon technician for radon testing. They will be able to give you more accurate readings faster, but usually at a greater cost. What Can I Do About the Elevated Radon Levels in My House?The most common radon-reducing strategy requires the assistance of a radon mitigation specialist. The specialist will install a radon mitigation system consisting of fans, pipe and accessories to vent the radon away from the home, into the outdoor atmosphere. Depending on the situation, the specialist will need to match the right strategy with the right circumstances. Some of these mitigation strategies include: aeration, GAC, sub-slab suction, sump-hole suction, or block-wall suction. Key TakeawayRadon is produced by the radioactive decay of uranium in the soil and can migrate upwards towards the surface. It can make its way inside your home through cracks, holes, gaps, penetrations, crawlspaces and others.
No matter where you're located in the world, when moving into a new house, you must test for radon regularly to keep your family safe from lung cancer. Finally, you should contact a radon mitigation specialist if the levels are close to or higher than the recommendations given by your national health authority. Radon's presence in homes is a matter of great concern because long-term exposure to high radon gas concentrations can lead to an increased lung cancer risk. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends that all homes be tested for radon and that corrective action be taken if necessary to reduce exposure. So what is a safe radon level? While there is no known "safe" level of radon, the EPA has set an action level of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) of air. This is the level at which the EPA recommends taking corrective action to reduce exposure. For all of our Canadian readers, 4pCi/L is equivalent to 148 Bq/m2. There are a number of ways to reduce radon levels in your home, and the type of corrective action you take will depend on the level of radon present and the type of home you have. Here's a closer look at radon levels and what you can do to reduce your exposure. Safe Radon Level: At a GlanceAs we mentioned earlier, there is no set "safe" level of radon. However, the EPA has set an action level of 4 pCi/L, which is the level at which they recommend taking action to reduce radon levels. The EPA's action level is based on the fact that if you are exposed to radon at this level over a long period of time, your risk of developing lung cancer is about 1 in 10,000. This might not seem very high, but it's important to remember that lung cancer is a very serious and deadly disease. So, while there is no "safe" level of radon, the EPA's action level is a good guideline to follow. If your home has elevated radon levels (above 4.0 pci l), you should take steps to reduce it. How To Check Your Home's Radon LevelIf you're concerned about radon in your home, the best way to find out if you have a problem is to test for it. Radon testing is simple and easy to do, and it's the only way to know for sure if you have a radon problem. There are two types of radon tests: short-term tests and long-term tests. Short-Term Radon TestsShort-term radon tests are typically used to test for radon over a period of 2-90 days. These tests are the most common type of radon test, and they're relatively inexpensive. Short-term tests can be done with either electronic monitors or charcoal canisters. Electronic monitors measure radon continuously and can be set to take readings over a period of days, weeks, or even months. On the other hand, charcoal canisters are placed in your home for a set period of time (usually 2-90 days) and then sent to a lab for analysis. If you use a short-term test, it's important to remember that radon levels can fluctuate from day to day and even from hour to hour. So, a single short-term test might not give you an accurate picture of your home's overall radon level. For this reason, we recommend using a short-term test first, followed by a long-term test if the results of the short-term test are 4 pCi/L or higher. Long-Term Radon TestsLong-term radon tests are used to test for radon over a period of more than 90 days. These tests are more accurate than short-term tests in terms of measuring your home's overall radon level. If you're thinking of buying a home, it's important to have a long-term radon test done before making the purchase. This will give you an accurate picture of the level of radon in the home and whether it needs to be mitigated. Long-term radon tests are typically done with either electronic monitors or alpha track detectors. Electronic monitors, as we mentioned earlier, measure radon continuously and can be set to take readings over a period of months or even years. Alpha track detectors, on the other hand, are placed in the home for a set period of time (usually 90 days) and then sent to a lab to be analyzed. Both types of long-term radon tests are considered equally reliable. The main difference is that electronic monitors tend to be more expensive than alpha track detectors. What is the Average Indoor Radon Level?The average indoor radon level in the United States is about 1.3 pCi/L. However, this number can vary significantly from home to home. In general, homes in the Midwest and Northeast have higher radon levels than homes in the South and West. This is because of the geological conditions in these regions. In some areas of the country, such as Colorado, Minnesota, and North Dakota, the average indoor radon level is closer to 3 pCi/L. In these states, it's estimated that 1 in 3 homes has a radon level above 4 pCi/L. If you live in an area with a high average indoor radon level, it's especially important to test your home for radon and take steps to reduce it if necessary. What Are the Health Risks of Radon?Breathing in air that contains radon can damage the lining of your lungs and lead to lung cancer. In fact, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States, behind smoking. Smokers who are exposed to radon have an even greater risk of developing lung cancer. This is because smoking damages the lungs and makes them more susceptible to the effects of radon. It's important to remember that radon is a radioactive gas, so it can't be seen, smelled, or tasted. The only way to know if your home has a radon problem is to test for it. If you're thinking of buying a home, we recommend having a radon test done before making the purchase. This will give you an accurate picture of the level of radon in the home and whether it needs to be mitigated. If you're already living in a home with elevated levels of radon, don't panic. There are things you can do to reduce the level of radon in your home and protect your health. These include:
Final ThoughtsWhile there isn't an official "safe" level of radon, the EPA recommends taking action to reduce your exposure if your home has a radon level of 4 pCi/L or higher. So, if your house has a radon level lower than that, you're probably in the clear.
Of course, the best way to know for sure is to test your home for radon and take action to reduce it if necessary. This will help protect your health and the health of your family. When it comes to keeping your family safe from radon, there is no such thing as being too cautious. This colorless, odorless, and radioactive gas can seep into your home through cracks in the foundation or other openings, and long-term exposure can lead to lung cancer. According to the EPA, radon is the leading cause of lung cancer in nonsmokers, resulting in about 21,000 deaths yearly. There is no safe level of radon exposure, so it's important to test your home regularly and take steps to mitigate the risk if elevated levels are found. So, how do you go about testing for radon? There are a few different ways, but the most common is with a radon test kit. These kits are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them an excellent option for most people. In this article, we'll take a look at five of the best radon test kits on the market. Let's dive in! The 5 Best Radon Gas Test Kits To Keep Your Family Safe1. Long-Term Radon Test KitWhen it comes to radon gas test kits, that's what we do! We strive to make every aspect of our product, and your experience, the best it could possibly be. That's why our product is at the top of the list! Our test kits are designed to be all inclusive, comprehensive, super accurate, quick, and very easy to use. All you have to do is open the package, place the test device in the lowest level of your home that is lived in regularly, and wait 90 days before sending it off to the lab. The lab will take care of the rest. Once they receive your return package, they will analyze the detector and then send you the results by email, as well as post it on your online account. After the 48-hour period is up, you simply seal the device in the included envelope and send it off to the lab for analysis. The results will be emailed to you within 72 hours of the lab receiving the device. We also sell a kit that is designed for short-term testing, one that is best used when/if you suspect that there may be elevated levels of radon in your home. For more accurate results than a short-term measurement, go with this option. We guarantee it won't disappoint. Pros:
Cons:
2. Airthings Wave Plus Smart Radon DetectorIf you're looking for a long-term or short-term radon detector, the Airthings Wave Plus is a great option. This battery-operated device can be placed on any flat surface in your home and will take readings continuously. We understand this option is not a radon test kit per say, but it is still a very popular radon monitor with great reviews. The Airthings Wave Plus uses Bluetooth to connect to your smartphone, so you can view the real-time results of the radon readings. You can also check the historical data to see if there has been an increase in radon levels over time. If the device detects elevated levels of radon, it will send you an alert to your smartphone so you can take action to mitigate the risk. What sets the Wave Plus apart from other radon detectors is its additional features, such as indoor air quality monitoring and temperature and humidity readings. Pros:
Cons:
3. AccuStar Charcoal Canister Radon Test KitThe AccuStar Charcoal Canister Radon Test Kit is another short-term testing option that is simple to use. Just like our Radon Test Kit, you'll place the device in the lowest level of your home, but for 2 days instead of 90 days. After the two days are up, you'll seal the device and send it back to the lab for analysis. Within a few days, you'll receive your results in the mail. Since all costs are included in the price of the kit, there are no hidden fees. One thing to keep in mind with charcoal canister test kits is that you can only use them once. So if you want to test for radon regularly, you'll need to purchase multiple kits. On the other hand, real estate agents or home buyers can use this one-time test to get a snapshot of the radon levels in a home. Pros:
Cons:
4. Airthings Corentium Radon MonitorWhile the Airthings Wave Plus is our top pick for a long-term radon monitor, the Airthings Corentium Home Radon Monitor is a close second. This device is similar to Wave Plus in that it will take continuous readings and send you alerts if elevated levels of radon are detected. However, what makes the Airthings Corentium Home stand out is its portability. This device is powered by AA batteries, so you can take it with you if you move to a new home or office. The clear digital display makes it easy to see both short-term and long-term trends in radon levels. A self-inspection report feature allows you to generate a PDF report of the radon readings, which can be helpful if you don't want to spend money on a professional inspection. The main difference between this device and a detector like the one in our Radon Test Kit is that it's less accurate because of the technology it uses to sense/detect the alpha particles that come from radon gas. Pros:
Cons:
5. Health Metric Radon Test Kit for HomeThe Health Metric Radon Test Kit for Home is another great option for those looking for an affordable, easy-to-use radon gas test kit. This charcoal-based test kit is designed for short-term testing and can be used to test for both radon gas and radon in water. Taking just a few minutes to set up, the Health Metric Radon Test Kit for Home comes with everything you need to get started, including clear instructions. Once the test is complete, simply mail the results back to the lab (postage is included), and you’ll receive your results within 3-5 business days. If you’re looking for a reliable and affordable radon gas test kit, the Health Metric Radon Test Kit for Home is a great option. Pros:
Cons:
Wrapping UpRadon gas testing is an important part of any home safety routine. By testing for radon, you can ensure that your home is safe for you and your family. The 5 radon test kits we've reviewed here are some of the best on the market and they will help find the answers you are looking for.
So why wait? Get testing! A passive radon system makes use of natural airflow and pressure differentials to remove radon gas from your house. These types of systems typically run from drain tiles/basement sump baskets up until the roof. Since there is no active fan involved in venting the radon, this system is termed as ‘passive’. These systems are completely noiseless and use no electricity. However, this does not make a significant difference as compared to their active counterparts due to the already low power consumption ratings. Home owners who do not want pipes running around their house, running the appeal; go for these mitigation systems. Let us know more about passive radon systems. How is Radon Harmful?Before we dive into passive radon systems, let us understand why one should invest in a mitigation system. Radon is a radioactive gas, whose solid particles get trapped in human lungs and damage lung tissue, causing lung cancer. In fact, radon is the second most common cause of lung cancer in the US. The EPA predicts that each year, roughly 21,000 Americans succumb to lung cancer linked to radon. What is a Passive Radon System?A passive radon mitigation system removes radon from your home without the aid of an active component by utilizing the natural pressure differential and outside air currents. They are not so common in newer houses, but can be commonly seen in older buildings since they can only be installed before the foundation is laid. Although installing passive systems properly during new construction is essential, it is not typically suggested as a stand-alone solution. Passive systems can only deal with low radon levels, but fail to be effective when the levels are high. Even the slightest modifications in the system can impact the performance severely. Active systems on the other hand, use an electric fan and are able to push out radon at a faster rate. The advantages that you get with these type of systems are:
How Does A Passive Radon System Work?In a passive radon system, radon normally escapes through the roof via a pipe from the sump crock or drain tile in the basement. Systems for measuring passive radon rely on the "stack effect". It works by moving air from a high pressure zone to a low pressure zone and vice versa. Difference in pressure causes movement of heavy radon particles. However, relying solely on the stack effect wouldn’t cut it. It normally isn't sufficient to considerably lower radon levels in a passive radon system because newer homes are now built airtight for energy efficiency. How Much Does A Passive Radon System Cost?Installing a new passive radon mitigation system can cost between $771- $1,185. This can go up to $3,000 in homes with complex layouts and larger sizes. Costs for radon mitigation systems are determined by a few parameters. Property’s size and design, climate, foundation type, location, labour expenses, permit fees, testing, inspection, and radon system type are a few of them. Converting a Passive Radon Mitigation System Into Active an Active SystemConverting a passive system only involves one step: Fitting a fan with the pipeline which can be connected with an outlet nearby. This can easily be done if you locate an electrical outlet and get a fan installed near that point. In some houses however, layout restrictions might come in the way of direct installation, which can make the process difficult. All in all, this depends on how your house is structured and whether or not you have a power outlet near the pipes. ConclusionA passive radon system is simply a no-fan version of a mitigation setup that does not take up any electricity and relies on pressure differences for ventilation. Though this system has its advantages when it comes to being noise-free, these are outweighed by how effective an active system can be.
Not only this, but an active system can also do a much better job at regulating radon levels in your house due to a dedicated component which prohibits radon particles from staying inside the system. As a homeowner in the United States or Canada, running consistent tests in your house for radon gas should be at the top of your maintenance routine. After smoking, radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer in America. Moreover, it has been found that one in every 15 homes in the United States have high radon levels. Luckily, most of these tests can be done without professional help using a wide range of radon detectors available today. Here are some of the best picks.
Among the listed radon detectors, the AirThings Corentium remains the overall best home radon detector based on user reviews. Radon Eye RD200Produced by Radon FTLab, the Radon Eye RD200 detector gives its results in minutes. Radon Eye guarantees that you will get a very reliable result in 60 minutes. This detector uses Radon Eye’s proprietary detection technology which gives 30 counts per hour per pCi/L. You can easily connect your Android/iOS device to the Radon Eye RD200 detector where your home test results will be visible. These results get updated every 10 minutes and you get an option to track monthly/weekly ratings. Key Features of the Radon Eye RD200
AirThings 2960 View PlusManufactured by AirThings, the AirThings 2960 View Plus gives an accurate radon measurement (+- 10%) at 5 pCi/L after 7 days. It uses a USB C cable, an air quality monitor, and 6 AA batteries for its operation. The battery cell is made of alkaline material and has an average battery life of 2 years. The AirThings 2960 View Plus also detects air pollution, temperature,CO2 levels, humidity, airborne chemicals, air pressure, and radon in its vicinity. The Wi-Fi connection lets the user synchronize test results easily with your mobile device. Test results can be viewed via their online dashboard as well. Key Features of the AirThings 2960 View Plus
AirThings CorentiumAlso developed by AirThings, the AirThings Corentium was the first battery-powered digital radon detector. It has a visual alarm indicator that warms when the radon level is increasing. The accuracy in test results improves after 7 days with an error margin 10% and 5% within 2 months. It uses 3 AAA batteries for its operation. The design of the internal monitor is taken from an advanced high-contrast technology normally seen in commercial detectors. The system is so reliable and robust that AirThings ships it with a ‘no-calibration required mark’ valid up to ten years. Key Features of the AirThings Corentium
Buyer's Guide For Radon DetectorsHere are some of the most important features to watch out for when buying radon detectors.
Frequently Asked QuestionsHere are some frequently asked questions about radon detectors. How Do Digital Radon Test Detectors Work?The radon test detectors work by tracking or counting the quantity of radon particles in the air. Digital radon test detectors make use of air sensors to identify alpha particles. They then count the number of these particles per hour, followed by determining the radon level. Where Can a Radon Detector be Placed?For the radon detector to work effectively, it should be put on the lowest point of elevation. Place it in a common room where you spend most of your time, such as the living room. ConclusionThe fact that we humans cannot detect radon gas does not mean it does not affect us. Prolonged exposure to radon gas increases an individual's chances of having lung cancer by 50%.
The above-listed radon monitors detectors are some of the best with an assurance of accurate test results; however, if you want the most accurate radon measurement possible, order one of our radon test kits here. Thanks for reading! Radon gas occurs naturally in soil. Radon can enter any home, regardless of how old your building is, its structural integrity, location (on the ground, in a crawlspace, or a cellar), or whether or not it is sealed. Radon levels are high in houses of all shapes and sizes, and consistent worldwide. The only way to determine the radon level in your home is through testing. This can be done by yourself using a DIY testing kit or by consulting experts. How Does Radon Gas Enter A House?Radon is formed when radioactive elements such as radium and radium decay. It can enter your home through various channels, including cracks and wall gaps. During the construction of houses, the foundation often comes in contact with this radioactive element, which, when it decays, finds its way into the building through holes in the foundation. Radon gas can also enter your home if your basement is in contact with rocks and natural stones such as granite containing this radioactive element. This dangerous gas can also be found in well water because wells sourced from an aquifer are in contact with the soil and rocks where Radon gas is present. When such water is used in the home for washing, bathing, and other activities, it builds up the Radon gas concentration in your home. Combating Radon Gas In HousesThe Department of Housing and Urban Development suggests taking the following extra steps to protect yourself against a radon problem and reduce the risk of developing lung cancer due to excessive radon gas levels in your house:
Radon Testing At HomeThe only sure way to know if you and your family are at risk of radon exposure is to have your home tested. To reduce the risk of radon problems, you can test for and reduce elevated radon levels by doing the following: Buying A Radon Testing KitYou can test your home using a DIY Radon Test Kit or hire radon reduction, assessment, and mitigation services to do the testing for you (This may cost you more, but radon mitigation is the best way to combat radon). Putting Your House Or Workplace To The Test It shouldn't take you too long to carry out the test, and it's inexpensive and straightforward. It entails opening a box and placing a small measuring instrument in a room for a specified amount of time. Short-term testing could take anywhere from a few days to several weeks. Long-term testing could take up to 90 days. The longer the test takes, the more relevant the results are to your environment and way of life. Sending The Radon Detection Kit To The Right SourcesFollow the testing kit package instructions to determine where to submit the device for results. What Effects Does Radon Exposure Have On Health?According to the EPA, in the United States, radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung disease. Many homes have high levels of radon, which may increase the risk of cancer and cardiovascular problems. Radonite enters the lungs whenever anyone breathes in radon. Radon and its decay products emit radiation in the form of beta and gamma rays. When radioactive compounds in the body emit alpha particles, they may be hazardous. Alpha particles could harm already vulnerable lung cells, increasing the likelihood of lung cancer. Important Things To NoteRadon Is Not Hazardous Outside, But It Is Very Poisonous When Enclosed Or InsideRadon concentration is often higher inside houses than outdoors because there is less indoor air and less room for radon gas to scatter and escape. Although radon exposure may occur in any kind of structure, Radon levels are often higher in cellars, vaults, and living areas in direct contact with the soil, Homes with good insulation and tight seals are more prone to accumulating radon to dangerous levels. Radon Gas Traces May Be Found In Springs, Wells, And Boreholes That Provide Groundwater Radon exposure may occur through the consumption of polluted water, but inhaling radon is usually more dangerous. It is more common to find elevated radon levels in groundwater such as springs as opposed to surface water such as lakes and streams. Radon levels in groundwater may be higher in homes that use that water source than in water that has been processed at a treatment plant. Frequently Asked QuestionsCan I Test My House For Radon?Yes. If you live in a place where radon levels are high, you need to have your home tested. The EPA believes that 6 million households in the United States now have hazardous radon levels. You can test for radon by employing an expert or purchasing a do-it-yourself test kit from a reliable radon test kit shop. Most radon gas testing kits include two-day or ninety-day tests that must be returned to the manufacturer for results. Where Does Most Of The Radon In Our Homes Come From? Radon may enter a building mostly through the earth or through cracks, construction joints, and openings. Radon gases are produced by soils and minerals. Excess radon may enter your house through water, building materials, and gas sources. What Is The Impact Of Radon On The Skin?Continuous skin exposure to high radon levels can lead to skin cancer. Radon emits carcinogenic radiation. Although this substance is neither invisible nor colorless, it might create issues for homeowners. Radon is among the leading cause of lung cancer in the United States and Canada. It may be visible at ocean level once it has been extracted from the soil. At low quantities, it readily evaporates outside and is typically not dangerous. How Frequently Should My House Be Tested? Environmental agencies recommend getting a radon test done before purchasing a property, after significant renovations, after a reduction or mitigation system has been put in place, and every two years after that. Final ThoughtsGiven the numerous ways this radioactive gas can enter your homes, such as leaks and cracks, Radon gas exposure should be taken seriously.
You shouldn’t wait until things are critical before conducting a test and taking precautions to reduce this threat to a safe level. According to the American Cancer Society, long-term exposure can damage lung tissue, increase the risk of developing lung cancer, and cause other health effects. With the option of a DIY Testing Kit, it is now simple to carry out this process and protect your family and loved ones. As you may or may not know by now, radon is a radioactive element derived from uranium, thorium, and other radioactive elements that decay in soil, rocks, and groundwater. Radon is a potentially toxic gas known for almost two centuries. It is an invisible, colorless, and odorless gas. Because of these features, radon cannot be detected using only human senses. The main attribute that has helped radon evade human research for many years is its invisibility. Since we tend to believe what we see and throw suspicion to what we can't see, the awareness around radon gas is slow to spread. The dangerous thing about radon is that it emits radiation in alpha particles that are potentially harmful to human health. What is more damaging is that after its alpha emission, it gets converted into certain daughter elements, which continue to release radiation in the lungs for decades. This article mainly focuses on the invisible story of radon and how this invisible gas is a potential threat to human health. Radon: The Leading Cause of Lung CancerRadon is one of the most extensively investigated human lung carcinogens. It has been known for several years as the potential cause of lung cancer among miners. However, radon does not remain confined to mines. Research also indicates that the number of cases of lung cancer due to residential exposure to radon ranges from 3,000 to 33,000, making it the second cause of lung cancer after cigarette smoking. Apart from lung cancer, radon exposure is also associated with other malignancies such as leukemia. According to the health authority, radon exposure is a category one cause of lung cancer. As other studies have shown, radon exposure is the second leading cause of death in patients with lung cancer. About 10 to 40 thousand Canadians succumb to lung cancer due to radon exposure every year. A statistical report also shows a significant rise in lung cancer cases, mainly due to the exposure of contaminants including radon, asbestos, and heavy metals. Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer After Radon ExposureThis story begins in an environment of high radon concentration. Whenever someone inhales air in such an environment, radon becomes trapped in the lungs. Radon disintegrates into its daughter radioactive elements in the lungs by releasing highly ionizing radiation (alpha particles). This radiation produces oxygen free radicals that damage the core of life – DNA (genetic material carrying complete life information)—the damaged DNA results in the development of mutations that are the primary setting for cancer. However, cancer takes decades to develop. In addition, other changes have been noticed in the lungs of patients who have only years of history of radon exposure. In these patients, the daughter elements of radon keep on emitting radiation in the lungs, resulting in the formation of fibrosis within the tissues. This fibrosis is the leading cause of restrictive lung diseases characterized by difficult inspiration. Signs & Symptoms of Radon ExposureAs you can't see, feel, or smell radon, you do not know when you are inhaling radon unless some signs or symptoms appear. Hence, it is pretty important to look for the early signs and symptoms of radon poisoning because if they are left untreated, they can lead to the development of lung cancer. The classical sign of radon poisoning is a persistent cough due to respiratory distress. Other pulmonary (related to lung) symptoms include recurrent attacks of bronchitis or pneumonia, coughing up blood, chest pain, wheezing, and hoarseness of voice. Some patients also report weight loss, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Whenever such symptoms arise, you must get yourself a thorough medical examination. Radon: Equally Disastrous to Smokers and Non-Smokers?A pronounced study clearly states the differential effects of radon exposure among smokers and non-smokers. According to this study, 260 out of 1000 smokers will develop lung cancer if exposed to 20 pCi/L of radon during their lifetime. Similarly, but not as bad, 36 individuals will develop lung cancer in every 1000 non-smokers. It is clear from this study that regardless of the potentially disastrous synergistic effect of smoking and radon exposure, radon exposure is more than enough to cause lung cancer. That’s why it is known as the element of risk. Every year, about 21000 deaths occur due to radon exposure, and only 2900 of those are non-smokers. How Damaging is Radon Exposure in Indoor Environments?Radon is an invisible gas that accumulates in closed buildings. More specifically, buildings with poor ventilation provide a more favorable environment for the dramatic accumulation of radon. Once it becomes concentrated within a confined area, it creates a lung cancer inducing situation similar to that which was observed in miners. Therefore, the most favorable radon concentration locations are the buildings' basements. As proven from various research studies, radon is a carcinogen found in homes, offices, warehouses, mines, etc. Therefore, all those who have several years of indoor radiation exposure due to radon are at risk of developing cancer and other lung disorders. Environmental Factors Influencing Indoor Radon ConcentrationSignificant data demonstrate the effect of environmental factors on radiation exposure by radon in indoor environments, including homes, schools, offices, and other buildings. One of the particular factors is the outdoor temperature. It has been observed that the indoor radon concentration is significantly higher in winter-autumn than in spring-summer. This detailed analysis further demonstrates that the indoor concentration of radon is inversely related to the indoor humidity, outdoor wind speed, and outdoor dew point temperature. It concludes that whenever indoor humidity is higher, there are fewer chances for the radon to accumulate in that area. In addition, rain has been observed to increase the radon concentration indoors. Indoor Sources of RadonThe primary sources of indoor radon includes soil gas, building materials, and tap water. Soil gas infiltration is by far the major contributor to indoor radon concentration. Here arises a question - How can we determine the points of entry for soil gas? The answer lies in the facts that are discussed later. Among soil particles, specific tiny spaces are filled with water or air in the ground. The gases that are occupying these spaces are collectively termed soil gas. Soil gas is composed of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. It also contains additional gases like nitric oxide, methane, and ammonia. Building materials like brick, marble, and granite have a basal level of radioactivity due to some radioactive minerals. They are also likely to possess radon in significant amounts, leading to a higher level of radiation. Drinking water is only a minor source of radon. Due to drinking contaminated water, radiation exposure is only associated with a negligible risk of stomach cancer and other gastrointestinal malignancies. Preventive Measures Against Radon ExposurePrimary health care providers must understand the role of radon in causing lung cancer and what precautions should be taken by the general public to avoid undesirable outcomes. These actions begin with getting your house tested for radon exposure. If you are following the E.P.A. radon exposure guideline of 4 pCi/L, and you test higher than that, then action is required to reduce radon levels and therefore minimize radon exposure. General Preventive MeasuresThe best cure to any illness is prevention. Individuals should be guided to quit smoking, as radon and smoking have a synergistic effect in causing lung cancer. Nutrition-rich fruits, high in antioxidants, and vegetables may also help the body fight the carcinogens. In some cases, carotenes supplements are also prescribed to individuals at risk of high radon exposure. These supplements lower the chances of cancer development. Environmental Measures to Reduce ExposureAccording to a statistical report, about 42% of radiation exposure worldwide is because of radon. To our surprise, only 0.9% of the global radiation exposure is because of the nuclear industry. It is clear from this finding that radon is dramatically increasing in our local environment and is causing severe health effects. Thus, it is the recommendation of health authorities to get buildings – houses, schools, offices, government - tested for the presence of radon. Environmental testing would be the best preventive measure against radon exposure, which would help to eventually reduce radon-related lung cancer cases because we would be able to identify which buildings require mitigation. References
Radon can easily get into your home through cracks and in the foundation of your home. While many people install a radon mitigation system to control radon levels, others try to use epoxy coating on the basement walls and basement floors as a method to combat elevated levels of radon. But are floor sealing systems any effective? If yes, then how would we seal cracks in the basement floor to stop radon? Stick till the very end of this article to find out! Radon Gas: An OverviewRadon is a radioactive gas formed by the break-down of radioactive elements such as uranium. This is a colorless, odorless, and an inert gas, which makes its detection quite tricky unless you are using a dedicated tool. This is a naturally occurring gas, so people are almost always exposed to it. It usually seeps into the buildings through the gaps and cracks in the basement and accumulates over time. Radon dilutes itself in the surrounding air, and then starts to cause many health problems. Prolonged exposure to radon increases the chances of lung cancer by 14%. According to the EPA, radon causes over 20,000 lung cancer deaths every year in the US alone. Can Radon Enter Your Basement?Radon usually enters your house through the basement, and it emanates when uranium found in soil naturally decays. Since it is produced from the soil, it finds easy access indoors through the cracks in your basement. The pressure difference between the outside and inside area of your home creates a vacuum. This vacuum pulls radon through the cracks or holes in your basement. Radon can enter your house through:
However, you will need a special instrument or test kits to accurately determine the concentration of radon in your house. Will Sealing My Basement Help?Yes, you can reduce the level of radon in your basement by sealing the cracks. The only prerequisite is that your house must have a radon mitigation system to manage the level of radon in the house. You must also keep in mind that you should seal the whole floor rather than the cracks. This is because, over time, the flooring can develop new cracks, allowing the radon to enter the house. Hence, covering the basement flooring with the help of the sealant reduces the changes of new cracks and reinforces the floor again. Also, as per the EPA, you must use a sub-slab depressurization system to remove all the radon gas present beneath the basement flooring before sealing it. This system extracts the extra radon and vents it off in the air with the help of the fan. Once the extra gas is removed, you can seal the basement floor and reduce the level of radon in your house. How To Seal The Cracks In The Basement FloorThe foundation of your house is one of its most important components. Thus, while laying down the foundation of the house, special emphasis is put on it, but no matter what you do, it develops cracks over time. Since these cracks are sufficient for the radon gas to escape into your house, it is essential to seal these cracks in the basement. You can follow these steps to seal the cracks in the basement floor for radon: 1. Clean The AreaBefore applying any sealant on the basement floor, you must clean the floor properly. Cleaning is essential so that the sealant can stick to the floor properly. You can prepare a solution of dish soap and warm water and then scrub the surfaces with the help of a scrub brush. If your floor has mold growth, you must use a bleach solution, mold remover, or baking soda solution for scrubbing. Once you have removed the mold, wait for the floor to dry so as to avoid mold growth again. In addition, if your floor has been painted over it, you must remove the paint with the help of a paint stripper. Once you have removed the paint, you can scrub the surface. 2. Check For OpeningsNext, you must locate all the openings and cracks on the flooring. These openings and cracks act as a place for the radon to seep in. Therefore, it is essential to waterproof the foundation and prevent possible leaks. You can fill these openings and cracks with caulk or hydraulic cement. After applying the mixture of caulk or cement, you must wait for the mixture to dry and solidify. 3. Checking The Surrounding Of The BasementYou must go through all the corners of your basement properly to identify any more cracks. You should also look for all the water sources present outside or inside the basement. Relocate all the plants and fix the damaged gutters and downspouts. 4. Applying The SealantOnce you are done with patching the basement floor and removing all the water sources, apply one to two coats of the sealant. You can choose the sealant as per the surface of the basement. Use a roller or paint brush to apply the sealant uniformly on the flooring. Summing UpRadon gas can enter your house through any gap, crack, or cavity in the wall. It becomes necessary to close the cracks and seal them. Otherwise, radon gas can harm you and your loved ones. Regularly inspect the flooring and the walls to ensure they have no holes or cracks.
Lastly, you should get your floor sealed even if you have a mitigation system in place already. This is because sealing helps in dehumidification, dust-proofs the slab and improves usability. If the area is too large, consider hiring a professional instead. Whether you've just moved into a new home or have been living in the same place for years, making sure that your home is safe from nefarious gases like radon is crucial for your family's health. After all, you want to be able to breathe easy in your own home, right? Fortunately, there are ways to test for the presence of radon gas, and we've got the scoop on the best long-term radon monitors out there. These monitors will help you get an accurate reading of the radon levels in your home without any lab fees. Although the results they provide are not as accurate as what a lab can produce, you will get a continuous reading that you can check at any time. So whether you're looking for an easy, no-fuss way to test your home for radon gas, or want to be extra sure that your family is safe, read on for our top 5 picks for the best short-term AND long-term radon monitors. The 5 Best Long-Term / Short-Term Radon Monitors For Your HomeLet's review the following electronic devices, all of which are equipped with sensors capable of short-term and long-term detection. Please keep in mind that this list is not in any particular order. No one device is better than another. They each have different features and different options. Your choice depends on your own personal preferences. 1. RadonEye RD200 Home Radon DetectorHaving accurate and continuous readings of the radon levels in your home is key to keeping your family safe, and the RadonEye RD200 Home Radon Detector does just that. This little gadget is designed to be placed in your home and will take readings every 10 minutes, giving you up-to-the-minute information about the radon levels in your home. Not only is the RadonEye RD200 easy to use, but it's also one of the most responsive radon monitor on the market. The OLED display is large and easy to read, even from a distance, and the free app (for iOS and Android) allows you to track the readings over time, so you can see if there are any spikes or changes. All in all, the RadonEye RD200 is a great choice for those who want quick, accurate, real-time readings of the radon levels in their home. Pros:
Cons:
2. Airthings 2930 Wave PlusWhat's better than a smart home device that can tell you the radon levels in your home? One that can also tell you the humidity, temperature and air quality of course! The Airthings 2930 Wave Plus does all that and more, making it one of the most comprehensive continuous radon monitor on the market. The most interesting feature of the Wave Plus is its "Wave" function, which gives users a color-coded visual of the air quality in their homes. Green means the air is good, yellow means it's moderate, and red means it's time to open a window! The accompanying Airthings app is also very user-friendly and gives users the ability to see trends over time and set up alerts if the radon levels in their homes get too high. Pros:
Cons:
3. SafetySiren Pro4If you're willing to dish out a bit more cash for a radon monitor, the SafetySiren Pro4 is a great option. This reliable and well-reviewed testing device has been on the market for years, so you know it's tried and true. The SafetySiren Pro4 is placed in your home and will take readings every 24 hours, giving you a good idea of the long-term radon exposure in your home. This device has an audible alarm that will sound if the radon levels in your home get too high, so you can take action immediately. Homeowners will love that the SafetySiren Pro4 is easy to use and gives them peace of mind knowing that they'll be alerted if the radon levels in their home get too high. Pros:
Cons:
4. Airthings Corentium Home Radon DetectorAnother great option from Airthings, the Corentium Home Radon Detector, is a reliable and user-friendly long-term radon test kit. Don't let the vintage cell phone appearance fool you — this little tester is packed with features. This detector will measure and log your indoor radon levels, giving you an accurate idea of what you're dealing with. You can only view short-term and long-term readings on the device's screen, but this simplicity can be great for those who want an easy-to-use machine. The Airthings Corentium Home Radon Detector is battery-operated, so you don't have to worry about cords or plugs. All in all, this is an excellent option for those looking for an affordable and user-friendly long-term radon test kit. Pros:
Cons:
5. Airthings 2960 View PlusWhile the Airthings Wave Plus is an amazing option for those looking for a comprehensive radon monitor, the Airthings View Plus takes things up a notch. This is the most expensive option on our list, but it's packed with features that make it worth the splurge. The Airthings View Plus is a cable-free device that can be placed anywhere in your home and will take continuous readings throughout the day. This means you can get an accurate idea of your home's radon levels at any time. Not only that, but the Airthings View Plus also monitors your home's temperature and humidity levels, as well as the air quality. The device's WiFi connectivity — which the Wave Plus lacked — means you won't have to deal with any cords or plugs. Pros:
Cons:
But What About Our Radon Test Kits?Every homeowner should be aware of the risks associated with radon exposure, and testing for radon is the only way to know for sure if your home is safe. While there are many different types of continuous radon monitors on the market, the 5 we've listed above are, in our opinion, the best of the best; however, if you want to ensure accuracy and reliability when conducting a radon measurement, then our short-term and long-term test kits are what you need. In addition, our radon test kits are certified by the government; therefore, the results produced by them will be accepted by any organization/company that depends on those said results to make a critical decision, like say a homebuilder for example.
Best of luck with your future decisions. Stay safe and live radon free! We all want what’s best for our families, and that includes keeping them safe from harmful gases/toxins. Radon is a radioactive gas that can be found in small amounts in the air we breathe. It is considered to be a leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers, and while it can’t be seen or smelled, it could be present in your home. Luckily, there are ways to discover your radon levels before mitigating them (by up to 90%) if they are found to be high. One of the most effective ways to do this is by installing a radon mitigation fan. Radon fans work by drawing air from beneath your home and releasing it through an exhaust pipe that goes above your roofline. This process effectively reduces the amount of radon in your home, making it a safer place for your family. Finding the best radon fan for your home can be a daunting task, but we’ve done the research for you. Here are the five best radon fans on the market, based on factors like price, features, and customer reviews. Top 5 Best Radon FansRadonAway 23032-1 RP260 Radon Mitigation FanRadonAway dominates the radon fan market, and the RP260 is their most popular model. It’s one of the more expensive fans on our list, but it’s also one of the most powerful, with a maximum airflow of 251 CFM (cubic feet per minute). The RP260 is designed for use in homes with 6” PVC pipes, and it can be used in both new construction and retrofit applications. It’s also backed by a 5-year warranty, which is one of the longest in the industry. This ultra-quiet fan operates at the same level as a soft whisper, and it’s rated for continuous use. It's also energy-efficient, which will save you money on your electric bill. Pros:
Cons:
2. Tjernlund RMS160 Sidewall Radon Mitigation SystemIf the 80+ years of experience Tjernlund has in the ventilation industry don’t put your mind at ease, maybe their 10-year warranty will. As the leading manufacturer of inline fans, Tjernlund is a name you can trust. Since the RMS160 runs via your basement sidewall, it’s one of the more discreet options on the market. You won’t have to worry about an unsightly fan in your yard, and the RMS160 can be installed without climbing on your roof. Consisting of an exterior hood, a plug-in fan, and an installer-purchased PVC pipe, the RMS160 is an all-in-one solution for your radon problem. It’s one of the more affordable options on our list but stays true to Tjernlund’s high standards of quality. Pros:
Cons:
3. Fantech HP 2190 Radon FanBudget-conscious homeowners will love the Fantech HP 2190. This radon fan is one of the most affordable on the market, but that doesn’t mean it lacks in quality or performance. The HP 2190 has a maximum airflow of 163 CFM, which is more than enough for most homes. This radon fan is designed for use in 4” or 6” PVC pipes, and it can be used in either horizontal or vertical applications. Installing the Fantech HP 2190 is a breeze, thanks to its plug-and-play design. Featuring a fully sealed plastic housing, this radon fan is designed for years of trouble-free operation. The welded seam housing also makes the HP 2190 one of the most durable radon fans on the market. Pros:
Cons:
4. RadonAway 2301101 XP201 Radon Mitigation FanAnother quality offering from RadonAway, the XP201 is a small but mighty fan that’s designed for use in 4” PVC pipes. It’s one of the most popular models for retrofit applications and is certified by the EPA for continuous operation. The XP201 is similar to the RP260 in many ways, but it’s a more affordable option. It’s also slightly less powerful, with a maximum airflow of 112 CFM. However, it’s still one of the most effective radon fans on the market. This radon fan is perfect for sub-slab mitigation systems since it’s designed for use in small spaces. The unique impeller and motor design make the XP201 one of the quietest fans on our list, and it’s backed by a 5-year warranty. Pros:
Cons:
5. Suncourt RDK04-3 Radon Fan Mitigation KitKnown for its home improvement and HVAC products, Suncourt is a name you can trust. The company's RDK04-3 radon fan mitigation kit includes everything you need to do a professional installation, all in one box. The highlight of this kit is the 4” Super Centrifugal Inline Fan, which is specifically designed for radon mitigation. It’s one of the most powerful fans on our list, with a maximum airflow of 200 CFM. The RDK04-3 also comes with a 4” to 3” reducer, 2 anti-vibration PVC couplers, plus an air pressure indicator. The thermal plastic resin insulation keeps the noise level down, and the built-in automatic thermal reset feature protects your fan from overloading. Pros:
Cons:
How to Choose the Best Radon Fan for Your HomeEven though we've rounded up some of the best radon fans on the market, you might be wondering which one of the models is the best fit for your home. Here are a few factors to keep in mind as you make your decision: AirflowThe first thing you'll want to consider is the airflow rating of the fan. This is usually measured in CFM (cubic feet per minute), and the higher the number, the better. Choosing a fan with too low of an airflow rating will make it less effective at reducing radon levels. Pipe SizeMost radon fan brands have models that accommodate 4”, 5", 6” PVC pipes, but there are a few models that can be used in smaller 3” pipes. Be sure to check the specifications of the fan before you buy it to make sure it will work with your existing system. Level of ProtectionSome radon fans come with housing that's been sealed with epoxy resin to prevent air leakage. If you live in an area with high radon levels, this is an important feature to look for. After all, you don't want your fan to be working overtime because of a leak. If you ever suspect a leak, you will have to do a smoke test to locate the leak and then seal it up. Bottom LineHaving a radon fan in your home is the best way to reduce radon levels and keep your family safe, but with so many different models on the market, it can be tough to know which one to choose.
We hope our list of the 5 best radon fans will help you narrow down your options and find the perfect model for your home. Remember to keep airflow, pipe size, and level of protection in mind as you shop around, and you'll be sure to find a fan that meets your needs. Radon detectors - alpha track detectors, continuous radon monitors, scintillation devices, etc. - give us an idea of the concentration of Radon in the atmosphere. This is an important metric as radon harms the human body and can cause many serious illnesses including lung cancer. To avoid over-exposure, you first have to know how much radon you are exposed to. To discover that, you need to perform a radon measurement. Many homeowners often get radon testing kits, or radon monitors, set up in their property. But how do Radon detectors work? Keep on reading to find out! How Do Radon Detectors Work?Charcoal radon test kits absorb radon gas over a period of 2-90 days and are then sent for sampling in a lab. This is the cheapest method you can use to detect radon. However, this is also the most inaccurate as radon gas concentrations may rise/fall overtime depending upon the weather, humidity, etc. Another tool used for radon detection is a continuous radon monitor. This device measures the radon gas in pCi/L and alerts the user if the value is above the set standard (4 pCi/L). This technology relies on sensors that pick up the alpha particles released by radon gas into the air. This information is then converted into representable data which is shown on the digital display of your detector. Detectors usually have a Teflon disc which is statically charged and stimulates when an ion generated from radon decay strikes it. This Teflon layer is then chemically treated to make the ion tracks visible. Unlike test kits that need to be sent out to labs, there are many radon detectors which take continuous readings and show the real-time findings on the screen. Properties of Radon GasNow that we know how a radon detector works, let us find out more about some properties of radon which makes it so unique. Radon gas is invisible, odorless, and tasteless; thus, detection becomes quite tricky unless one uses a tool instead of relying on their senses. The United States Environmental Protection Agency advises having your house tested for radon before purchasing or renting it. You can test for radon using "DIY" test kits or you can contact professional technicians and testers. However, any test you choose for detecting radon should be officially certified. You can do the testing on a short-term basis (two to ninety days) or a long-term basis (90 days to a year). Keeping an interval between tests is essential as radon levels fluctuate depending on the time of day, the season, weather patterns, and the changes in pressure. Suppose you need the findings of a test immediately. In that case, conducting a short-term test is preferable. That said, long term testing will provide more accurate results. These detection systems are usually installed in the basement since radon gas typically seeps into a house via the basement. Radon Detector: Working PrincipleRadon detectors detect alpha particles that fire off from the radon gas in order to calculate the concentration of radon gas. In other words, radon emits alpha particles, which are then detected by devices that come with a sensors tuned to catch the presence of alpha particles. The sensor, termed a "photodiode," is the digital equivalent of film, producing a "radon image" based on the number of particles that strike the sensor. Afterwards, the lab examines the alpha track by triggering a chemical change and then calculates the markings on the foil in order to determine the radon concentration and give you an accurate reading. Types of Radon DetectorsThere are a plethora of Radon detectors available on the market and this section will help you understand the inner-workings of different detectors to help you choose the type tailored for your needs. Alpha Particle DetectorsA radon-tight device is a tiny piece of specially manufactured plastic substrate encased within a filtration chamber that prevents radon penetration. Whenever the photodiode sensor picks up traces of radon, they mark areas of damage on the foil called residual alpha traces. Chemical peeling from the foil magnifies the alpha traces and renders them visible under an optical microscope. It is then counted with an atom sensor to get an accurate Radon concentration in the desired location. Continuous Radon Monitoring SystemsContinuous Radon Monitors (CRMs) utilize sensors like scintillation chambers and pulse ionization to detect Radon. These radon monitors scan the environment for radon with a tiny pump or by letting air permeate into the detector’s sensor compartment. These monitors come with an electrical circuit that keeps a log of data and calculates the cumulative radon content after specific time intervals. Electronic Radon DetectorsMost electric radon detectors use a silicon sensor for detecting alpha particles released by the radon. Due to the small diffusing cell, constant waiting periods are necessary for detecting accurate radon levels.
The electric detectors use the high-voltage output mechanism to capture chargeable radon, allowing the silicon sensors to work at higher sensitivity for precise radon readings. In case you still have questions, maybe you will find your question and its answer in this list of 9 most commonly asked questions regarding radon and radon testing. If you can't find an answer to your question, send us an email and we will respond to it promptly - [email protected] Where should a radon test be placed?The idea is to measure the radon concentration on the lowest livable part of your house. Therefore, if your basement is the lowest livable area, then place it in your basement. If your basement is not suitable for living or spending significant time, then do not place the radon detector in the basement. If you have a basement AND a crawlspace, we recommend placing a second radon detector on the floor directly above the crawlspace area. Where can I find radon testing near me?You can order a DIY radon test kit through this website. We will have it delivered to you no matter where you are. Find out which radon test kit you need here. What causes radon gas in homes?Radon exists in every single home everywhere. Radon gas is caused by the breakdown of uranium deep in the ground. It finds it way up through the ground and into your home through any crack, hole, gap, pit, or penetration through the foundation that it can find. It will build up in your home over time, so it's important to measure the radon concentration in your home. Where is radon most commonly found?Radon can be found in every house, warehouse, apartment building, condo, office building, or any type of building for that matter. Radon concentrations are the highest in the lowest level of the building, which is commonly the basement; however, if you have a crawlspace, your radon levels will most likely be the highest in the crawlspace. How do you detect radon in your home?Radon can be detected using an alpha track detector like the one included in this radon test kit, or you can use a continuous radon monitor, which is an electronic device, to constantly monitor the radon concentration in your home. What does radon smell like?Unfortunately, radon has no smell. Also, you cannot see, hear, taste or feel radon. The only way to detect radon is by using a radon detector. How many radon test kits do I need?Under normal circumstances, you only need one radon test per house. Under rare circumstances, you may need 2 or even 3 radon detectors. If your house is abnormal, or if you have a crawlspace, send us an email and describe it - [email protected] How often should you test for radon?The authorities recommend testing your house every 5 years How long does a radon test take?Our short-term radon test takes at least 10 days and no longer than 90 days. Our long-term test takes at least 90 days to a year.
Though people in countries like Canada are becoming more and more aware of radon’s presence in their home and taking measures to stop it from affecting their indoor air quality, the radon-driven health issues are still increasing. Radon exposure leads to various, severe illnesses including respiratory and lung diseases. Also, radon affects the resale value of the home. It is difficult for an ordinary person to determine the presence of radon within the home premises. In this article, we will share useful information about what radon is, how it affects health and how you can identify its presence in your home. It also highlights why radon tests in homes in Toronto are important. If you suspect Radon presence in your home, it’s time to hire a professional radon inspection service in Toronto, Canada.
About Radon Radon gas is inert, colorless and odorless. Radon is naturally in the atmosphere in trace amounts. Outdoors, radon disperses rapidly and, generally, is not a health issue. Most radon exposure occurs inside homes, schools and workplaces. Radon gas becomes trapped indoors after it enters buildings through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Indoor radon can be controlled and managed with proven, cost-effective techniques. Radon in a negligible amount is not harmful; however, breathing it in for a long time can be very toxic. But as the technology is evolving, there are ways to mitigate radon gas risks. There are a few ways that can help you keep the Radon gas level in your home to a minimal level. Is Radon Present In Your Home? How Should You Do A Radon Measurement? Yes, radon is present in your home and there are chances that the level is rising. You may never feel the need to measure or test your home for radon gas. However, there are two very simple ways to test your home for radon gas. The first is to use the innovative radon measurement kits. If you plan to do it, you should carefully follow all the instructions given in the user manual. The second method is to hire a professional team or individual to perform radon testing in your home. It is a more reliable way, as professional Radon testing service providers are experienced and have extensive knowledge. However, make sure that they perform a long-term test (minimum 3-months) for more accurate results. Radon Exposure – How does it happen? Radon exposure risks apply when a person inhales considerable amounts of radon over a long period of time. Radon levels in the home, office, school, or other confined structures can be low or high. We spend the majority of our time at home. Radon can infiltrate your home through gaps in the foundation, floor cracks, or wall cracks. As soon as the toxic gas enters the home, it gets strapped inside and accumulates to dangerous levels. Irrespective of the structure, radon exposure can happen in any home. Surprisingly, radon levels rise to a dangerous level in an insulated home, which is built on the soil containing uranium, thorium, and radium. Radon experts in the United States quantify the gas in pCi/L, and anything above 4 pCi/L is considered dangerous. According to estimates, 1 out of every 15 homes has higher radon levels. So, there is a possibility that your home may also have higher levels. Radon concentrations are often highest in the basement or on the lowest floor of a house. How Does Radon Affect Your Health? Radon Gas can become toxic if inhaled for a long period. It gets inside the lining of the lungs and emits radiation. Over time, these radiations damage the lungs to the point of no recovery, which results in lung cancer. After smoking, radon is the second big reason for lung cancer. On average approximately 20,000+ people die of lung cancer caused by radon exposure. So, it is something we should take seriously. Indicators of Radon Exposure Since Radon is a colorless and odorless gas, it becomes difficult to identify its presence right away. The health issues become visible after some time and with consistent exposure to the radon. The major health concern is lung cancer, which may only become visible after years of exposure. Lung cancer may begin as a persistent cough, difficulty in breathing, or asthma. Other symptoms are coughing up blood, chest pain, and weight loss. Call your doctor if you detect any of these symptoms. Unfortunately, there are no medical tests that can indicate that you have been exposed to radon gas. Also, no treatment can eliminate it from the body once inhaled. However, if you feel that you are exposed to high levels of radon, you must take action immediately. Usually radon detectors can be effective to test radon levels inside any home. Radon detectors are used by professional Radon testing companies in Toronto. Prevention of Radon Poisoning There are a few reliable ways that can save you from toxic radon gas exposure. First of all, you should get your home tested for the presence of radon gas. It will help you verify the level of radon in your home. You can either get radon test kits that are widely available in the market or hire a professional radon testing service. The advanced and affordable test kits seem viable options for checking radon levels for a short-term or long-term. To avoid the exposure in the long run, it is suggested to hire a professional Radon testing service. According to the experts, long-term tests are more reliable because radon gas levels in the home fluctuate with time. So, a long-term test will calculate the concentration of Radon more precisely. If radon is reaching unsafe levels in the home, then you must hire a professional to do Radon elimination processes. Radon Mitigation Methods Used by Professionals Soil suction method This approach uses a radon fan and a vent pipe to extract radon from beneath your home and exhaust it to the outside. Enhanced ventilation method Make sure your home has a well-planned ventilation system so that air can move freely in and out. Also, prevent any methods that can transfer the radon from the lower level to other floors of the home. Radon sump mechanism In this method, a void beneath the floor and a pipe are installed. The fan then draws the radon gas out from the home. Positive pressurization This approach blows fresh air inside the home, which keeps the indoor air under constant positive pressure. Making your residence sealed will not reduce radon pollutants until you adopt other precautionary measures. However, everyone should examine their homes and, if necessary, install adaptive measures. Facts About Radon Gas That Every Homeowner Should know An uninvited guest that enters your home Radon gas seeps into your home without letting you know. It is odorless and colorless. It is formed when uranium, which is a radioactive element, breaks down. It mostly enters the home from the soil on which your home is built. So, the lower floors are the most exposed to radon gas. Some countries have high radon levels. Radon is present in every building, but the concentrations are usually modest. Homes in some areas of the country may have greater levels, and it depends on the type of land/soil. Levels may be higher in countries with lots of rock in the ground. Reducing Radon Levels is not a complicated task Though high radon levels can cause severe health issues, the good news is that these levels are easy to reduce. Wrong perception is imprinted on people’s minds that it is going to cost them a fortune. Well, nothing is more expensive than human life. There are a few simple approaches as discussed earlier that can be followed to reduce radon levels in the home. The cost depends on the method and the type of home you own. Radon mitigation measures include either ventilating the radon out of the house by applying a negative pressure or by maintaining a positive air pressure in the house to prevent radon from entering. Most treatments work for a long time and simply need to be checked regularly. Immediate action is necessary for unsafe radon level If we inhale an enormous amount of radon for an extended period, this exposure can cause harm to our lungs, increasing our chance of lung cancer. Also, if you smoke and live in a radon filled home the chances of lung cancer are doubled. That is why, if you have high radon levels in your house and smoke, you must take action. Final Thoughts Remember that radon gas is present everywhere. When a high radon level is identified, you should consult an expert. When an elevated radon level is discovered, addressing the issue might help safeguard the value of the home and the lives of the residents. Looking for a professional radon inspection service provider in Toronto Canada? Contact Us. |
AuthorI am a professional radon technician who enjoys writing about radon to spread awareness of this harmful, radioactive gas. Archives
February 2023
Categories
All
|
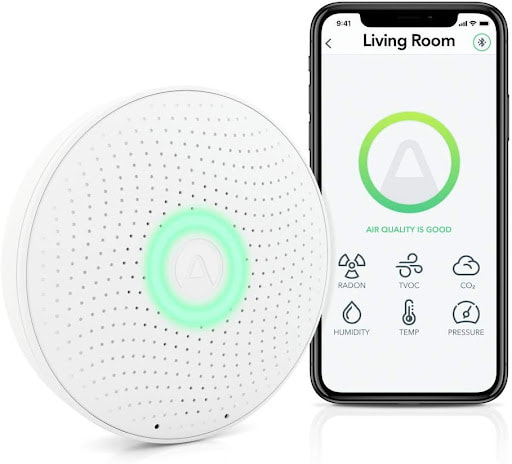
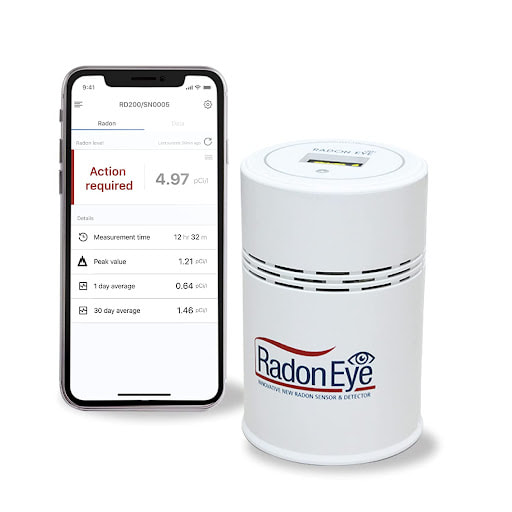
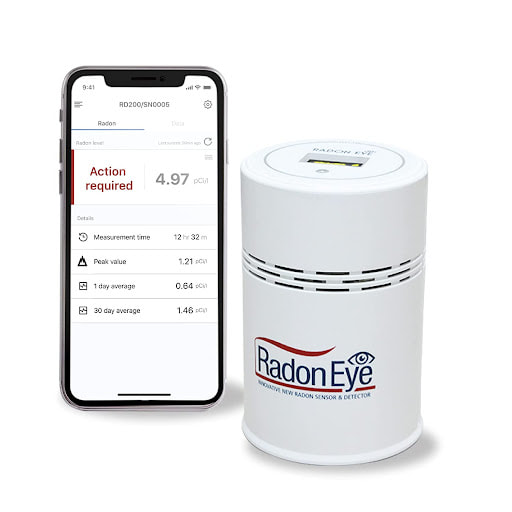












































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
